Blog > How Inflation Affects the Housing Market

Ever wondered about the intricate connection between inflation and the housing market? Surprisingly, they are closely intertwined, and changes in one can significantly influence the other. Let's dive into this intriguing relationship.
The Connection Between Housing Inflation and Overall Inflation
Shelter inflation is a specific measure of price growth in the housing sector. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) conducts a survey among renters and homeowners to gather this data. Renters report their rental costs, while homeowners estimate the rent they would charge for their homes if they were not living in them.
Just as overall inflation gauges the cost of everyday goods and services, shelter inflation examines the cost of housing. Recent survey results indicate that shelter inflation has been on a downward trend for four consecutive months (see graph below).
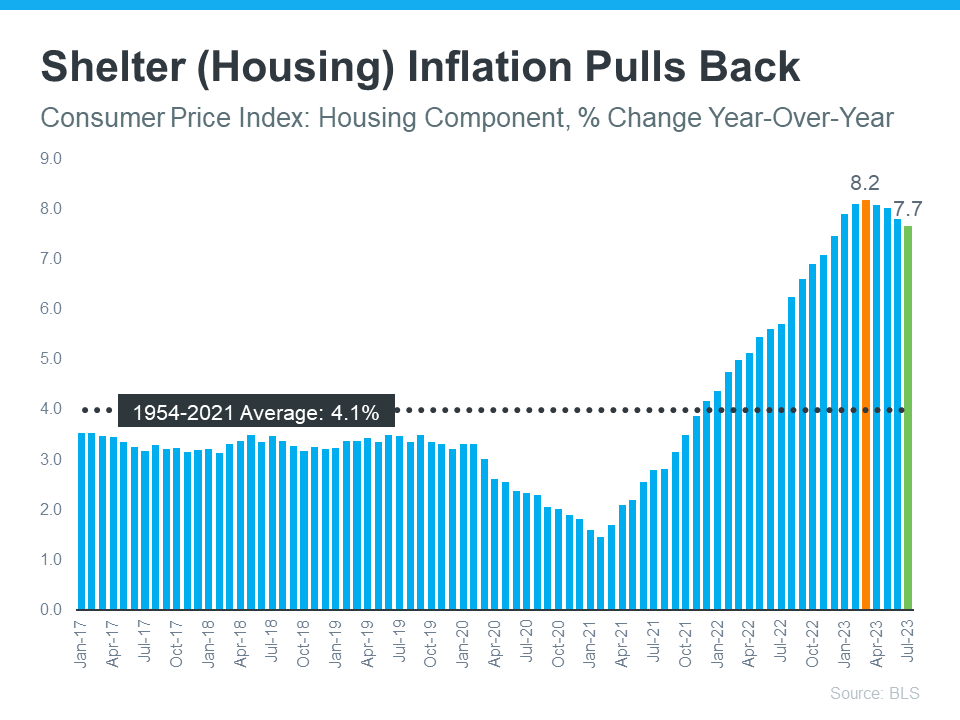
Why is this significant? Well, shelter inflation constitutes approximately one-third of the overall inflation rate as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI). Consequently, fluctuations in shelter inflation can lead to noticeable shifts in overall inflation. This suggests that the recent decline in shelter inflation might signal a potential drop in overall inflation in the coming months.
This moderation in inflation would be a positive development for the Federal Reserve (the Fed). Since early 2022, the Fed has been actively working to rein in inflation. While they have made some progress (it peaked at 8.9% in the middle of last year), their ultimate goal is to reach a 2% inflation rate (the most recent report indicates 3.3%).
Inflation and the Federal Funds Rate
So, what steps has the Fed taken to combat inflation? They have raised the Federal Funds Rate. This interest rate directly influences the borrowing costs for banks when they borrow money from each other. When inflation began to rise, the Fed responded by increasing the Federal Funds Rate to prevent the economy from overheating.
The graph below illustrates the dynamic relationship between inflation (blue line) and the Federal Funds Rate (orange line). Whenever inflation starts to climb, the Fed raises the Federal Funds Rate to steer it back toward their 2% target.
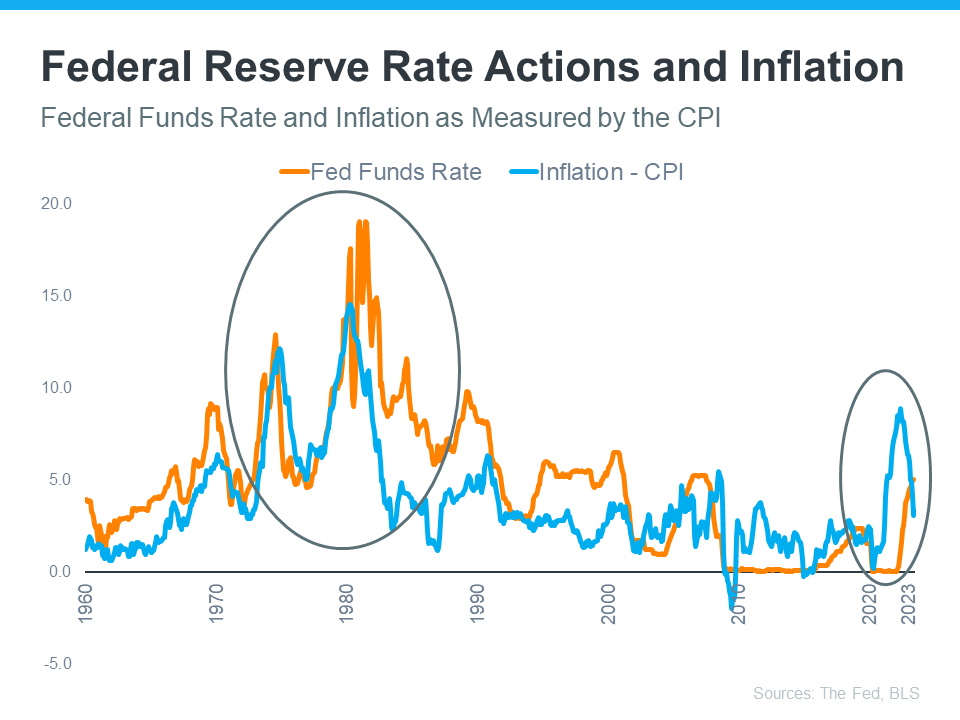
The circled portion of the graph showcases the most recent surge in inflation, the Fed's measures to raise the Federal Funds Rate to counteract it, and the subsequent moderation in inflation as a response to these actions. As inflation approaches the Fed's current 2% target, they may not need to further increase the Federal Funds Rate substantially.
A Brighter Outlook for Mortgage Rates?
So, what's in it for you? While the Fed's actions do not directly determine mortgage rates, they exert an indirect influence. As explained by Mortgage Professional America (MPA):
"... mortgage rates and inflation are connected, however indirectly. When inflation rises, mortgage rates rise to keep pace with the value of the US dollar. Conversely, when inflation subsides, mortgage rates follow suit."
While predicting the future of mortgage rates remains uncertain, it's heartening to see signs of inflation moderating in the economy.

